Are we still talking about container plants or are you still moving the goal posts?
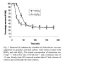
it was in sealed glass to insure equilibrium of all contaminants. the media was then filtered ina centrifuge ensuring the highest accuracy. this test is bullet proof. clay is a soil type that readily attracts these heavy metals and the fact that plain water coudl have this much of an impact speaks volumes on the benefits of flushing.
"MATERIAL AND METHODS Batch tests were performed according to the ASTM Standard D3987 to determinethe removal of Cr, Ni, and Cd from two different clayey soils using variousextracting solutions (ASTM, 1996). Soils Two clayey soils, kaolin and glacial till, were used in this study. Kaolin was obtainedfrom the American Clay Mineral Society. It is a low buffering soil consisting ofmainly kaolinite clay mineral (l00% fines). Glacial till was obtained from a site nearChicago, Illinois. It is a high buffering soil consisting of 31% quartz, 13% feldspar, 35% carbonates, 15% illite, 4 to 6% chlorite, 0.5% vermiculite, and trace amounts of smectite. The high carbonate content of this soil is mainly responsible for the highacid buffering capacity. In terms of grain sizes, glacial till consists of 16% sand and84% fines. The initial average pH values measured according to ASTM D4972(soilzwater ratio 1:1) were 5.0 for kaolin and 8.0 for glacial till. The kaolin is free oforganic matter, while the glacial till contains 2.8% organic matter (ASTM D2974).The cation exchange capacity is 1.6 meq/100g for kaolin and 18.0 meq/100 g forglacial till (Method 9080 in USEPA, 1986). The detailed test procedures and prop-erties of these soils were reported by Reddy et al. (1997). Contaminants The soils were spiked with Cr(III), Ni(II), and Cd(II) to simulate typical electro- plating waste constituents. Chrornic chloride, nickel chloride, and cadmium chlo- ride were used as sources of the Cr, Ni, and Cd, respectively, for both soils. Thesoils were spiked by adding these chemicals dissolved in deionized water to the air-dried soils. The resulting moisture contents were 35% for kaolin and 25% forglacial till. After the preparation of the contaminant-spiked soils, they were placedin
sealed glass bottles and refrigerated. The soils were equilibrated for at least 2weeks. The initial contaminant concentrations were measured based on the USEPAacid digestion procedure followed by analysis with atomic absorption spectropho-tometer (USEPA, 1986). The concentrations of Cr, Ni, and Cd based on the dry soilweight were 684 mg/kg, 340 mg/kg, and 230 mg/kg in kaolin and were 764mg/kg, 414 mg/kg, and 246 mg/kg in glacial till, respectively
Extraction was performed with a liquids to solids ratio (L/S) of 10:1. Themixture was stirred constantly for 1 h using a magnetic stirrer, and then thepH and redox potential of the soil slurry were measured using a digital pH/ORP meter. It should be noted that equilibrium conditions may not exist after 1 h of mixing (Griffin et al., l977a,b); however, the 1 h mixing time was selected to investigate the easily removable Cr, Ni, and Cd fractions and tocompare the relative removal efficiencies by various extractants. The soilsolids were separated by centrifuging at 4000 rpm for 10 min and thenfiltering using a Whatman No.1 filter paper. The supernatant was analyzedfor Cr, Ni, and Cd concentrations using an atomic absorption spectrophotom-eter according to USEPA methods 7190, 7520, and 7130, respectively (USEPA,1986). All tests were performed in duplicate in order to ensure the reproduc-ibility of the test results."
"Plus, while you're on a cadmium kick, shouldn't you be warning people to not use kelp meal? Very high in cadmium. For instance, Dyna-Gro Bloom has .2 ppm Cd, while Down to Earth Kelp Meal has 1.6 ppm, and E.B. Stone Kelp meal has 2.8 ppm!
I guess the lesson is don't use kelp meal?"
ECO-NEREO KELP .2-1-1 LIQUID FERTILIZER Date Sampled: 4 /9 /2009
Arsenic
0.509
Cadmium
0.08
Cobalt
0.16
Lead
1.6
Molybdenum
0.08
Nickel
0.32
Selenium
0.02
Zinc
<< < < < < 17.6
the lesson here is do your research and make your own decisions. and why are you comparign a bloom nutrient with a source of trace?