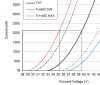
Decyphering the current/voltage chart on datasheets
- Thread starter Rahz
- Start date
stardustsailor
Well-Known Member
Rahz
Well-Known Member
The graph is from the Vero29 datasheet, same sheet that lists the voltage @ 85C I cited.
http://www.bridgelux.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/DS33 Bridgelux-Vero 29 LED-Array-Data-Sheet 2014.02.03.pdf
Your pic looks like the VeroV2 datasheet?
http://www.bridgelux.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/DS33 Bridgelux-Vero 29 LED-Array-Data-Sheet 2014.02.03.pdf
Your pic looks like the VeroV2 datasheet?
stardustsailor
Well-Known Member
Read carefully ....
Red line is the minimum value-and not the typical one- at Tc=85 C
Red line is the minimum value-and not the typical one- at Tc=85 C
stardustsailor
Well-Known Member
Please let me know if anything in the whole universe has a FIXED value ...
Pi ( π ) number ?
The golden section ?
The mass of Earth ?
The density of water ?
Element's atomic numbers ?
The speed of light ?
How long a second lasts ?
A kilogram ?
" Typical" ..Just for reference and only .
Nothin' is "fixed" in a universe that constantly "flows" ,"expands" , "pulses" & "vibrates" ...
Cheers.

Pi ( π ) number ?
The golden section ?
The mass of Earth ?
The density of water ?
Element's atomic numbers ?
The speed of light ?
How long a second lasts ?
A kilogram ?
" Typical" ..Just for reference and only .
Nothin' is "fixed" in a universe that constantly "flows" ,"expands" , "pulses" & "vibrates" ...
Cheers.

Rahz
Well-Known Member
Understood, but still confusing since the first dotted line intersects 2100ma with 36.4V That's somewhat close to the Tj85 typical but still a meaningful difference. If you intersect the Tj25 voltage with 2100 on that chart it's nowhere near any of those curves.Read carefully ....
Red line is the minimum value-and not the typical one- at Tc=85 C
So if you wanted to determine the max voltage at .7 or 1.4A what use is that chart?
nogod_
Well-Known Member
Dont worry about the chart if you find it confusing.....just use table 5.
Understood, but still confusing since the first dotted line intersects 2100ma with 36.4V That's somewhat close to the Tj85 typical but still a meaningful difference. If you intersect the Tj25 voltage with 2100 on that chart it's nowhere near any of those curves.
So if you wanted to determine the max voltage at .7 or 1.4A what use is that chart?
Greengenes707
Well-Known Member
Coming from the same company that doesn't bin their chips...interesting!
nogod_
Well-Known Member
Income? The US electoral process? My cat?
the speed of light in a vacuum is fixed and so are atomic numbers, thankfully haha
stardustsailor
Well-Known Member
For the speed of light in vacuum :the speed of light in a vacuum is fixed and so are atomic numbers, thankfully haha
Firstly the terms "distance" and "time" are not constant regarding their units.
Typical values only .S.I. or new S.I. and after some years from now a new S.I might pop-up ...
"
Increased accuracy of c and redefinition of the metre and second
See also: History of the metre
In the second half of the 20th century much progress was made in increasing the accuracy of measurements of the speed of light, first by cavity resonance techniques and later by laser interferometer techniques. These were aided by new, more precise, definitions of the metre and second. In 1950, Louis Essen determined the speed as 299,792.5±1 km/s, using cavity resonance. This value was adopted by the 12th General Assembly of the Radio-Scientific Union in 1957. In 1960, the metre was redefined in terms of the wavelength of a particular spectral line of krypton-86, and, in 1967, the second was redefined in terms of the hyperfine transition frequency of the ground state of caesium-133.
In 1972, using the laser interferometer method and the new definitions, a group at NBS in Boulder, Colorado determined the speed of light in vacuum to be c = 299792456.2±1.1 m/s. This was 100 times less uncertain than the previously accepted value. The remaining uncertainty was mainly related to the definition of the metre.[Note 8][105] As similar experiments found comparable results for c, the 15th Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) in 1975 recommended using the value 299792458 m/s for the speed of light.[137]
Defining the speed of light as an explicit constant
In 1983 the 17th CGPM found that wavelengths from frequency measurements and a given value for the speed of light are more reproducible than the previous standard. They kept the 1967 definition of second, so the caesium hyperfine frequency would now determine both the second and the metre. To do this, they redefined the metre as: "The metre is the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299792458 of a second."[80] As a result of this definition, the value of the speed of light in vacuum is exactly 299792458 m/s[138][139] and has become a defined constant in the SI system of units.[11] Improved experimental techniques that prior to 1983 would have measured the speed of light, no longer affect the known value of the speed of light in SI units, but instead allow a more precise realization of the metre by more accurately measuring the wavelength of Krypton-86 and other light sources.[140][141]
In 2011, the CGPM stated its intention to redefine all seven SI base units using what it calls "the explicit-constant formulation", where each "unit is defined indirectly by specifying explicitly an exact value for a well-recognized fundamental constant", as was done for the speed of light. It proposed a new, but completely equivalent, wording of the metre's definition: "The metre, symbol m, is the unit of length; its magnitude is set by fixing the numerical value of the speed of light in vacuum to be equal to exactly 299792458 when it is expressed in the SI unit m s−1."[142] This is one of the proposed changes to be incorporated in the next revision of the SI also termed the New SI.
"
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speed_of_light
Vacuum ?
"Perfect vacuum is an ideal state of no particles at all. It cannot be achieved in a laboratory, although there may be small volumes which, for a brief moment, happen to have no particles of matter in them. Even if all particles of matter were removed, there would still be photons and gravitons, as well as dark energy, virtual particles, and other aspects of the quantum vacuum."
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vacuum
There's not such thing as "Perfect Vacuum" ..
So neither is the speed of light a "fixed constant" ,in reality .
Only high precision typical value there...
As for the atomic number of elements ...
Since all elements do not exist in "pure " form ,but at their "purest"
are a "mixture" of their ISOTOPES,there's not such thing as Fixed atomic number .
Another ideal situation .
( The only "fixed" values in Universe is the language of values itself ...
The numbers themselves and the quantity they express.
Altough ,between two numbers ,infinite numbers exist .
From 1 to 2 ,there are infinite numbers ...
The terms "constant " and "fixed" exist only in an " ideal" universe.
The ideal universe of imagination (fantasy ) , hidden inside the human mind.
Cheers.

Last edited:
stardustsailor
Well-Known Member
No bins ,just typical values and a "declination from typical range" .Coming from the same company that doesn't bin their chips...interesting!
"cause if we research it further ,then some companies should have the bin of a bin ,of a bin ...
And so on ...
Or anyone has thought that LEDs/COBs of the same bin are exactly the same ?
Nope.
The correct term (the one Osram-Sylvania is using ) is " groups" .
Power group ,luminosity group and so on ..
Based on the limitations & restrictions of human vision and measuring instruments.
Cheers.

stardustsailor
Well-Known Member
Use the Typical values.Understood, but still confusing since the first dotted line intersects 2100ma with 36.4V That's somewhat close to the Tj85 typical but still a meaningful difference. If you intersect the Tj25 voltage with 2100 on that chart it's nowhere near any of those curves.
So if you wanted to determine the max voltage at .7 or 1.4A what use is that chart?
Cheers.

Greengenes707
Well-Known Member
No one has ever said that a bin is specific value of output. It is a range, or groupNo bins ,just typical values and a "declination from typical range" .
"cause if we research it further ,then some companies should have the bin of a bin ,of a bin ...
And so on ...
Or anyone has thought that LEDs/COBs of the same bin are exactly the same ?
Nope.
The correct term (the one Osram-Sylvania is using ) is " groups" .
Power group ,luminosity group and so on ..
Based on the limitations & restrictions of human vision and measuring instruments.
Cheers.

And also...I would bet that the speed of light is constant....how we measure it, not so much. But light will do what it does regardless if mankind can define and measure it.
Last edited:
uzerneims
Well-Known Member
This sounds like a mind-blowing poem!Please let me know if anything in the whole universe has a FIXED value ...
Pi ( π ) number ?
The golden section ?
The mass of Earth ?
The density of water ?
Element's atomic numbers ?
The speed of light ?
How long a second lasts ?
A kilogram ?
" Typical" ..Just for reference and only .
Nothin' is "fixed" in a universe that constantly "flows" ,"expands" , "pulses" & "vibrates" ...
Cheers.

That is why, people are arguing strongly, not living in flow, because world is flowing, and things are not constant, but everyone tries to prove his FIXED value, so that's why there is wars.
SupraSPL
Well-Known Member
The chart in your first post is an earlier version of the Vero PDF (02/0314). The old PDF is what shows up when you google "Vero 29 pdf", but you can get the updated PDF (09/12/14) that SDS cited by going to the Vero site. The updated PDF fixed the erroneous graph so it more closely matches the chart.Understood, but still confusing since the first dotted line intersects 2100ma with 36.4V That's somewhat close to the Tj85 typical but still a meaningful difference. If you intersect the Tj25 voltage with 2100 on that chart it's nowhere near any of those curves.
So if you wanted to determine the max voltage at .7 or 1.4A what use is that chart?
Last edited: