Actually its CBD that turns into THC. The turpenes and phenols in head of the trichomes combine to form CBC and CBG. CBG turns into CBD, and CBD turns into THC.
Really?
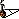
THC BIOSYNTHESIS
It is known that cannabinoids such as THC are originally
generated in acidic forms. In fresh tissues, the concentration of
THC is much lower than that of Δ1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid
(THCA). THCA is later decarboxylated by a non-enzymatic
reaction during storage or smoking (Yamauchi et al. 1967).
Despite the long history of marijuana research, the cannabinoid
biosynthetic pathway was elucidated only recently. Studies
on biosynthetic enzymes over the last decade have revealed
the THCA biosynthetic pathway as shown in Fig. 1. Cannabigerolic
acid (CBGA), a precursor of THCA, is the product of
the alkylation of olivetolic acid with geranyl pyrophosphate by
an enzyme called geranylpyrophosphate

livatolate geranyltransferase
(Fellermeier and Zenk 199

. Then, CBGA is converted
into THCA by a novel enzyme called THCA synthase
(Taura et al. 1995a). THCA synthase catalyzes a unique oxidative
cyclization of the geranyl group of CBGA. Recently, we
have successfully cloned THCA synthase and characterized its
structural and functional properties (Sirikantaramas et al.
2004). Biochemical characterization demonstrated that THCA
synthase is a flavinylated oxidase that requires molecular oxygen
and produces THCA and hydrogen peroxide. In addition,
we have already constructed transgenic tobacco hairy roots
expressing THCA synthase that can produce THCA upon feeding
of CBGA, suggesting a strategy for the biotechnological
production of THC (Sirikantaramas et al. 2004). However, the
metabolic engineering of the cannabinoid pathway requires a
detailed understanding of the biosynthetic mechanism including
regulation and trafficking of the enzymes involved in the
pathway. In this study, we describe the cell-specific localization
and possible physiological function of THCA synthase, the
enzyme responsible for THC production.
Fig. 1 Biosynthetic pathway of THC. CBGA is a product of the
alkylation of olivetolic acid with geranyl pyrophosphate. THCA
synthase catalyzes the oxidative cyclization of the monoterpene moiety
of CBGA to form THCA. THCA is decarboxylized to THC by a
non-enzymatic reaction. The responsible enzymes are: geranylpyrophosphate:
olivetolate geranyltransferase (1) and THCA synthase (2).









 livatolate geranyltransferase
livatolate geranyltransferase