Lucky Luke
Well-Known Member
always a good read
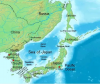
"The impact of the Soviet declaration of war and invasion of Manchuria and Sakhalin Island was quite different, however. Once the Soviet Union had declared war, Stalin could no longer act as a mediator — he was now a belligerent. So the diplomatic option was wiped out by the Soviet move. The effect on the military situation was equally dramatic. Most of Japan’s best troops had been shifted to the southern part of the home islands. Japan’s military had correctly guessed that the likely first target of an American invasion would be the southernmost island of Kyushu. The once proud Kwangtung army in Manchuria, for example, was a shell of its former self because its best units had been shifted away to defend Japan itself. When the Russians invaded Manchuria, they sliced through what had once been an elite army and many Russian units only stopped when they ran out of gas. The Soviet 16th Army — 100,000 strong — launched an invasion of the southern half of Sakhalin Island. Their orders were to mop up Japanese resistance there, and then — within 10 to 14 days — be prepared to invade Hokkaido, the northernmost of Japan’s home islands. The Japanese force tasked with defending Hokkaido, the 5th Area Army, was under strength at two divisions and two brigades, and was in fortified positions on the east side of the island. The Soviet plan of attack called for an invasion of Hokkaido from the west".
It didn’t take a military genius to see that, while it might be possible to fight a decisive battle against one great power invading from one direction, it would not be possible to fight off two great powers attacking from two different directions. The Soviet invasion invalidated the military’s decisive battle strategy, just as it invalidated the diplomatic strategy. At a single stroke, all of Japan’s options evaporated. The Soviet invasion was strategically decisive

 foreignpolicy.com
foreignpolicy.com
"The impact of the Soviet declaration of war and invasion of Manchuria and Sakhalin Island was quite different, however. Once the Soviet Union had declared war, Stalin could no longer act as a mediator — he was now a belligerent. So the diplomatic option was wiped out by the Soviet move. The effect on the military situation was equally dramatic. Most of Japan’s best troops had been shifted to the southern part of the home islands. Japan’s military had correctly guessed that the likely first target of an American invasion would be the southernmost island of Kyushu. The once proud Kwangtung army in Manchuria, for example, was a shell of its former self because its best units had been shifted away to defend Japan itself. When the Russians invaded Manchuria, they sliced through what had once been an elite army and many Russian units only stopped when they ran out of gas. The Soviet 16th Army — 100,000 strong — launched an invasion of the southern half of Sakhalin Island. Their orders were to mop up Japanese resistance there, and then — within 10 to 14 days — be prepared to invade Hokkaido, the northernmost of Japan’s home islands. The Japanese force tasked with defending Hokkaido, the 5th Area Army, was under strength at two divisions and two brigades, and was in fortified positions on the east side of the island. The Soviet plan of attack called for an invasion of Hokkaido from the west".
It didn’t take a military genius to see that, while it might be possible to fight a decisive battle against one great power invading from one direction, it would not be possible to fight off two great powers attacking from two different directions. The Soviet invasion invalidated the military’s decisive battle strategy, just as it invalidated the diplomatic strategy. At a single stroke, all of Japan’s options evaporated. The Soviet invasion was strategically decisive


The Bomb Didn’t Beat Japan. Stalin Did.
Have 70 years of nuclear policy been based on a lie?






